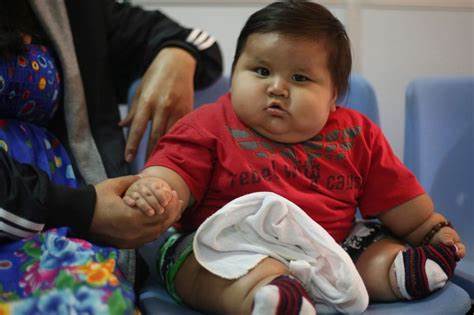
Childhood obesity is a medical disorder that is defined by an excess of body weight in children, when a child weighs more than what is appropriate for their age and height, they have a critical and complicated health concern. A child’s body mass index (BMI) can be used to assess if they are overweight or obese. The calculation of a child’s BMI involves dividing their weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters, to find the child’s BMI percentile, the resultant value is compared to growth charts that are unique to age and gender. Obesity is often defined as having a BMI percentile at or above the 95th percentile in children.
Childhood obesity is caused by several causes, including an unhealthy Diet: Eating a diet heavy in fats, carbohydrates, and calories but low in vital nutrients can cause weight gain. Lack of Physical Activity: Being sedentary, which includes spending too much time on screens and not moving about much, can lead to weight gain. Genetics: A child’s predisposition to obesity may be influenced by their genetic makeup. A child may be at greater risk if their parents or other near relatives are obese. Environmental Factors: A child’s weight can be influenced by their living conditions, which include having access to wholesome food and physical activities. Psychosocial Factors: Stress and family dynamics are two examples of emotional and psychological elements that might lead to unhealthy eating patterns and inactive lifestyles.
MUST READ;6 Things to Do During a Heat Wave
Here are six (6) ways that obesity can be managed and prevented in children;
- Encourage healthy eating practices; Educate Children on Nutrition, and explain to them the significance of different dietary types and nutrients. Describe the advantages of a healthy diet for their development and general welfare. Include Kids in Meal Planning, let kids help with meal planning and preparation. They may become more interested in eating healthily as a result, and they will feel more in control of their decisions.
- Promote frequent exercise; Find Fun Activities by determining what kinds of activities kids like to do, such as hiking, biking, dancing, or sports. Making exercise enjoyable raises the possibility of sustained participation. Also, make physical activity a part of your daily routine, some ideas are to go on walks, play active games, or engage in leisure sports as a family.
- Limit screen time; Decide how much time should be spent on screens each day and promote other pastimes and activities like reading, playing outside, or taking up creative hobbies. Establish Tech-Free Areas this is important to reduce sedentary behaviors, designate some areas of the house—such as the dining room or bedrooms—as tech-free zones.
- Provide nutritious snack options; Provide a variety of healthful snack options in the pantry and refrigerator to assist kids in selecting wholesome options. Encourage Intelligent snacking, children should be taught the distinction between “occasional” sweets and “everyday” food. Motivate them to make thoughtful decisions.
- Portion Sizes; Use visual aids to help children learn about acceptable portion proportions. For example, have them compare the size of a dish to their hand or common household items. Avoid Thinking Like a “Clean Plate”: Instead of having them eat everything on their plate, teach them to pay attention to their bodies and stop eating when they are full.
- Ensure adequate sleep; Establish bedtime routines, to assist kids in winding down and obtaining enough sleep. Avoid them using electronics right before bed as they can disrupt their sleep cycle.
Obesity in children poses several health issues, such as a higher chance of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other conditions. Additionally, it may result in negative social and psychological effects like low self-worth and a poor body image. In summary, promoting a nutritious diet, encouraging regular physical activity, and addressing the underlying causes of unhealthy behaviors are all part of the multidisciplinary approach to preventing and treating pediatric obesity.